Electroretinography (ERG)
Why is Electroretinography Important?
What is electroretinography (ERG)?
Electroretinography is an electrophysiological test of the retina, the layer of the eye which detects light. The electroretinogram (ERG) is to the retina what the electrocardiogram (ECG) is to the heart. Just as an ECG is crucial to diagnosing illness and monitoring the heart’s function, ERG plays a critical role in the care of the eye, and is instrumental in the early detection of retinal dysfunction.
Why does ERG matter?
Electroretinography provides a wealth of objective, vital information about retinal function and health. ERG plays a vital role in the diagnosis of acquired and inherited eye diseases, as well as fuel research into the factors that affect the health of the retina or the visual pathways.
What is an Electroretinogram?
The electroretinogram (ERG) is an examination that evaluates the function of the eye’s retinal cells. Patients’ eyes are stimulated with light and the resulting electrical activity from their retinal cells is measured by skin or corneal electrodes. Dependent on the type, intensity and colour of the light stimulus information on different areas and types of cells can be obtained.
3 Types of ERG Tests
There are 3 main types of ERGs: full-field flash ERG (ffERG), pattern ERG (PERG), and multifocal ERG (mfERG). Each has different applications and benefits. Determining the functional status of the retina with different typs of ERG testing allows clinicians and researchers to evaluate patients for retina-related conditions, reliably monitor retinal function over time, and evaluate the efficacy of retinal treatments. ERGs are used in human care, veterinary practices, and medical research.
Detect Functional Stress
Anticipate Structural Damage
How is ERG different than structural imaging?
Electroretinography objectively evaluates the functional abnormalities of the retina, while structural imaging shows the anatomy of the retinal tissue. While both functional and structural assessments have their benefits, functional changes generally appear well before structural changes. Catching retinal abnormalities quickly is critical for minimizing damage and maximizing vision retention, so functional assessments like ERG are important tools in the ophthalmic diagnostic suite.
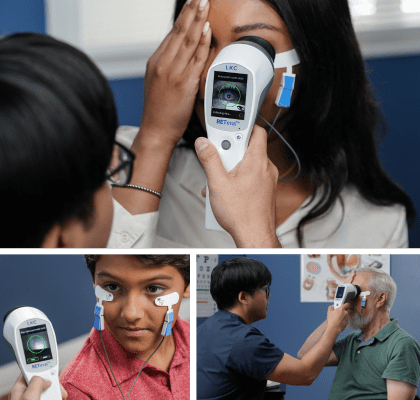
Handheld ERG as a practical & effective diagnostic tool
Recent studies comparing ERG to structural imaging techniques show that ERG is an effective diagnostic tool. In studies comparing ERG and structural imaging’s abilities to evaluate sight-threatening diabetic retinopathy, the handheld and portable RETeval device’s ERG results outperformed the traditionally-used imaging technique in predicting which patients would later need medical intervention.[13],[14] In an assessment of RETeval’s ability to evaluate diabetic retinopathy, the advantages of RETeval included earlier detection of retinal dysfunction, lower investment costs, and less required reading knowledge than the traditionally-used imaging technique.[15] An assessment of RETeval’s ability to evaluate central retinal vein occlusion found that RETeval ERGs are less invasive, easier to perform, and give more reliable predictions than the traditionally-used imaging technique.[16]
Advantages of ERG testing
The ease and sensitivity of ERGs performed with the handheld RETeval is highly preferred over imaging techniques in certain situations. Patients who have media opacities, poor cooperation, or small pupils are better able to be evaluated for retinal abnormalities with the RETeval[14].
Non-invasive ERG testing
In an independent study comparing RETeval ERGs to conventional digital retinal photographs, the RETeval was chosen by patients as the method preferred over photography.[14] While many children need to be sedated to undergo conventional ERG, children as young as six months old have been able to remain calm during ERGs performed with RETeval.[18] The non-invasive nature of the ERG and the ease of the hand-held, non-mydriatic RETeval makes the ERG device a valuable screening tool for many ophthalmic pathologies.
RETeval, ERG Testing Made Simple
Applications of Electroretinography
Electroretinography has an impressive range of human and animal applications, for both clinical and research uses. Our technology provides reliable, repeatable, and effective ERG solutions in all of these categories.
More about the RETeval ERG/VEP device
Popular Topics: Make a Difference in Diabetic Retinopathy Care | Glaucoma Evaluation with RETeval PhNR Test | RETeval Device Reference Data | RETeval in Optometry
Case Studies: ERG Demonstrates Stable Function Despite Severe Structural Damage | ERG Supports Treatment Decision in Diabetic Retinopathy | Photopic Negative Response as a Reliable Method for Glaucoma Follow-up in Children | A Tale of Two Patients | Vision Complaints Reflected on ERG | Predictive Value of Combining Diagnostic Technologies| ERG Provides Clarity When Fields and OCT Are Inconclusive| ERG Raises Red Flag, Changing Management Trajectory | ERG Provides Confidence to Monitor or Treat | ERG to Determine Ischemic Status | ERG to Replace FA for CRVO Treatment Decision | Using ERG to Monitor Glaucoma | Routine ERG Use Supports Complex Patient Management | ERG Alters Follow-up Schedule and Education for Patient with Diabetes | Using ERG for Management of Birdshot Chorioretinopathy | Using ERG to Monitor Glaucoma | Comprehensive Pediatric Assessment Using ERG in Challenging Cases | ERG Above and Beyond Retinal Imaging | ERG’s Role in Diabetic Retinopathy Progression Monitoring | ERG-based Risk Assessment in CRVO | ERG Supports Diagnostic Accuracy in a Pediatric Patient
Ebooks: Core Cases from the Clinical Compendium | Modern Fundamentals of Diabetic Retinopathy Management in Optometry | Elevating Patient Care with ERG
Articles: Electroretinography Added to AAO’s Diabetic Retinopathy Preferred Practice Pattern Guidelines | How Comfortable is the RETeval for Patients? |The Use of RETeval ERG/VEP in Pediatric Ophthalmology | How RETeval ERG Has Enhanced My Practice | The Use of RETeval ERG/VEP in Pediatric Ophthalmology | The Ultimate Guide to Diabetic Retinopathy in Primary Eyecare | What Type of Functional Testing Do You Prefer for Patients with Diabetes? | Major Milestone: RETeval Referenced in over 200 Publications | Collaboration to Elevate the Standard of Care for DR | Is ERG Needed if You Have Access to a Good Structural Imaging Device? | A Straightforward Approach to Managing and Supporting Patients with Diabetes | Simplify Grading and Risk Assessment in Diabetic Retinopathy | Simplify Daily Decision-Making with Modern ERG | Objective Functional Testing Needs in Diabetes and Glaucoma | Why Modern ERG is Re-Defining Diabetes Management | Diabetic Retinopathy Management Protocols for Optometry
Videos: RETeval: More Information, Better Decisions | RETeval: Eliminating Confusion in Clinic | RETeval: Function to Rely On | RETeval Handheld ERG: Features & Benefits | RETeval: Enhancing Collaborative Care | Handheld ERG for Primary Eyecare | Advice for Optometric Colleagues about Handheld ERG | Making a Difference in Diabetic Retinopathy Care | Changing the Way We Think About Electrodiagnostics | ERG Testing Made Simple | VEP Testing Made Simple | ERG Waveform | Introduction to Visual Electrophysiology | A Superior DR Progression Risk Assessment with the RETeval Device | Improve Glaucoma Management with the RETeval Handheld ERG Device | Reshaping the Retinal Diagnostic Landscape | New Solutions for Infants with ROP | Using the RETeval in Myopia Research
Webinars: ABCs of ERG | Ready for RETeval | ERG in Action | Blueprint for Functional Assessments | Predicting Vision Loss in a Busy Retina Practice | Objective, Functional Testing for Glaucoma? | Best Management Practices for Diabetic Retinopathy | How the RETeval Device Became a Daily Instrument in my Diagnostic Toolkit